Micro 3PL vs Traditional 3PL
Traditional 3PLs were built for scale. Micro 3PLs are built for speed, proximity, and adaptability.
Introduction
Traditional third-party logistics (3PL) providers were designed for scale, storage efficiency, and national distribution. For decades, this model worked well for palletized freight, wholesale distribution, and predictable replenishment cycles.
However, modern commerce has changed. E-commerce, omnichannel retail, rapid delivery expectations, and urban demand concentration have exposed limitations in centralized logistics. In response, a new operating model has emerged: the Micro 3PL.
Micro 3PLs are not smaller versions of traditional warehouses. They represent a structural shift toward localized fulfillment, distributed inventory, and AI-assisted logistics decisions. Understanding the differences between these two models is critical for brands choosing the right fulfillment strategy.
Micro 3PL vs Traditional 3PL: Comparison Table
| Factor | Traditional 3PL | Micro 3PL |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Size | Large regional or national distribution centers | Small, strategically placed urban or regional nodes |
| Inventory Placement | Centralized inventory stored in bulk | Distributed inventory positioned close to customers |
| Technology Stack | WMS and TMS with limited predictive intelligence | AI-driven forecasting, routing, and real-time optimization |
| Delivery Speed | 2–5 days typical for last-mile delivery | Same-day or next-day in core service areas |
| Cost Structure | Lower storage cost per pallet, higher last-mile costs | Optimized last-mile costs, leaner inventory overhead |
| Ideal Use Cases | Wholesale, B2B, low-velocity SKUs, national replenishment | E-commerce, DTC, urban delivery, omnichannel fulfillment |
This comparison highlights a key truth: neither model replaces the other outright. Each solves different logistics problems.
Operational Differences: Centralized vs Distributed Logistics
Traditional 3PLs rely on centralization. Inventory is consolidated into large facilities to maximize storage efficiency, labor utilization, and inbound freight economies of scale. Orders are then shipped long distances to reach end customers.
Micro 3PLs operate on distribution, not consolidation. Inventory is intentionally split across multiple smaller locations positioned near demand centers. Orders are fulfilled from the closest node, reducing transit time and last-mile complexity.
Operationally, this changes everything:
- Shorter pick-pack-ship cycles
- Reduced carrier handoffs
- Fewer delivery zones per order
- Faster recovery from regional demand spikes
Distributed logistics prioritizes responsiveness over bulk efficiency.
The Technology Gap: Where Micro 3PLs Pull Ahead
Technology is the primary differentiator between Micro 3PLs and legacy models.
Traditional 3PL technology stacks typically focus on:
- Warehouse execution
- Order processing
- Carrier booking
- Static inventory rules
Micro 3PLs rely on AI-assisted decision systems, including:
- Demand forecasting at the ZIP-code or neighborhood level
- Dynamic inventory rebalancing between nodes
- Intelligent order routing based on cost, speed, and capacity
- Predictive labor and carrier performance analytics
Rather than reacting to orders, Micro 3PLs anticipate demand, allowing them to operate smaller facilities with higher throughput efficiency.
When Traditional 3PLs Still Make Sense
Despite the advantages of Micro 3PLs, traditional 3PLs remain the best option in several scenarios:
- Bulk palletized inventory with low SKU complexity
- Non-urgent replenishment cycles
- National or international distribution from a single origin
- Manufacturing or wholesale supply chains
- Cost-sensitive storage-heavy operations
For these use cases, large centralized warehouses provide unmatched economies of scale.
When Micro 3PLs Win
Micro 3PLs excel where speed, proximity, and flexibility matter most:
- Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands
- Urban and metro-focused distribution
- Same-day or next-day delivery requirements
- Omnichannel retail fulfillment
- Regional demand spikes and seasonal volatility
In these environments, proximity to the customer is more valuable than warehouse size.
Enterprise Infrastructure Behind Micro 3PLs
While Micro 3PLs operate locally, they cannot scale without enterprise-grade logistics infrastructure. Carrier access, compliance, customs knowledge, systems integration, and national coordination are still required.
This is where established operators such as International 3PL play a critical role. Enterprise 3PLs provide the operational backbone that allows Micro 3PL networks to function cohesively, scale regionally, and integrate with global supply chains.
In practice, Micro 3PLs and enterprise 3PLs work best together, not in competition.
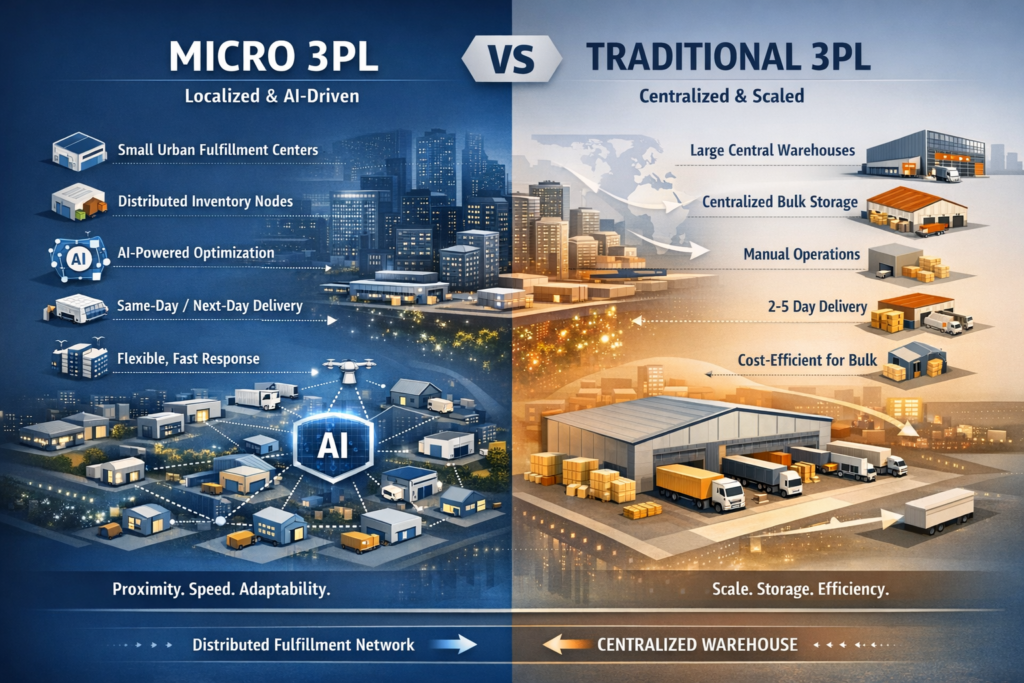
Micro 3PL vs traditional 3PL comparison showing distributed AI-driven fulfillment versus centralized warehousing
Is a Micro 3PL replacing traditional 3PLs?
No. Micro 3PLs are not replacing traditional 3PLs; they complement them. Traditional 3PLs remain essential for bulk storage and national distribution, while Micro 3PLs address localized, time-sensitive fulfillment needs.
Which model is cheaper?
Neither model is universally cheaper. Traditional 3PLs often have lower storage costs per pallet, while Micro 3PLs can significantly reduce last-mile delivery expenses. The total cost depends on order velocity, delivery speed requirements, and customer geography.
Can Micro 3PLs scale nationally?
Yes, when supported by enterprise logistics infrastructure. Micro 3PLs scale through networks of localized nodes, coordinated by centralized systems rather than a single massive warehouse.
Are Micro 3PLs only for e-commerce?
No. While e-commerce is a primary driver, Micro 3PLs are also used for omnichannel retail, subscription services, localized distribution, and time-critical fulfillment across multiple industries.
Final Note
Micro 3PLs represent an evolution in logistics strategy, not a rejection of traditional models. As fulfillment becomes faster, more localized, and more data-driven, businesses that understand when to deploy each
A Micro 3PL is a localized, AI-driven fulfillment model that distributes inventory across small facilities near customers to reduce delivery time and last-mile costs.
Traditional 3PLs optimize for centralized scale, while Micro 3PLs optimize for proximity, speed, and adaptability.
Micro 3PLs perform best in urban, omnichannel, and time-sensitive fulfillment environments where delivery speed outweighs warehouse size.
Micro 3PLs scale through networks of coordinated local nodes supported by enterprise logistics infrastructure rather than a single massive warehouse.
